
The Complete Guide to SEO
What is SEO?
SEO Definition: SEO is stands for Search Engine Optimization. Basically, it’s the tactics and techniques used to increase your website’s visibility on search engines to increase and improve the quality and quantity of visitors to your site or blog. Specifically, it is the optimization of…
- Page names (URLs)
- Headings and sub-headings
- Image ALT-tags
- Meta descriptions
- Anchor text links (internal and external)
- Keyword density of the page
The more visibility a site has, the more likely it is to get more organic traffic it will get from search engines. A ‘Focus Keyword’ would be selected for each page of the site and then included in the elements listed above.
Selection of each Focus Keyword comes from keyword research to find appropriate terms for the site. These keywords guide what content gets created and what kinds of organic traffic may be attracted as a result.
How Google Works

It used to be that you could rank just about any website for fairly broad keywords by using them in page titles and headlines and spreading them through your content, adding them to your meta-keywords list and your meta-description.
That was a few hundred million websites ago and hundreds, if not thousands, of algorithm updates ago.
What we did then, not only will not work today, those tactics might actually get you banned from Google.
To be honest, some of the ‘best practices’ from even a year or 2 ago simply don’t work.
They’re a waste of time.
Your time.
Would you like to know about SEO best practices, effective online marketing and search engine optimization tips that work today?
Complete Guide to SEO 2020
GOALS, TARGETS
We don’t completely know how the Google search algorithm is set up. We have made some educated guesses after trial and error or reading patents acquired by the Google’s parent company.
We have access to Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines. More on that below.
Most of us think of major updates, like Panda and Penguin, but in reality, ‘The G’ makes thousands of updates every year – many fairly minor and without much consequence.
What is the ‘job’ of your Search Engine Optimization efforts? What are your goals?
Who do you want to do what?
What are Google Ranking Factors?
SEOs believe there are 200 or more Google Ranking Factors. They probably include…
- Relevance? Does the post thoroughly cover what was being searched? Is the content comprehensive? Blogger riffs don’t rank well. Content must match needs.
- Quality backlinks and internal links. Google admits this is important. It likes to see incoming links from authority sites.
- User Experience (UX). CTR, Duration. Google has the data from your site and others. Google knows what was clicked on in the SERPs and how often.
- E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) Signals of the experience and expertise of both the author and the website. (See more below)
- Use of Images
- Outbound Links. Link to authority sites.
- Content Age
- Social Signals
- Site Structure
 Content gets an initial ranking which changes over time. It often takes months (35-40 weeks) for content to get ranked to its fullest extent.
Content gets an initial ranking which changes over time. It often takes months (35-40 weeks) for content to get ranked to its fullest extent.
Google monitors how visitors interact with the site, who links to it or shares it socially. It will compare it to what’s happening with other content in the niche. Sites that have been around a couple of years don’t take quite as long to rank content for.
Unfortunately, new websites will not rank well even if they have the best content. It takes time.
And it takes content. Lots of it.
This is why most people fail at blogging and SEO. They give up too soon. They need to write dozens of blog posts.
And wait.
Images are important in story-telling, but they are important for two other reasons:
- They can be optimized for SEO by including Focus Keywords in the filename and meta-descriptions of each image. I like to include an image for the top 2-3 keywords I’m trying to rank for.
- Images lead to more social shares on Facebook and Twitter. (More on sharing below)
It gets complicated.
Ranking factors are thought to be different for different industries or niches.
In fact, a 2019 Sparktoro survey of more than 1,500 SEO marketers weighed in on key ranking factors. 66.3% said they believe the weight of Google ranking factors varies by query.
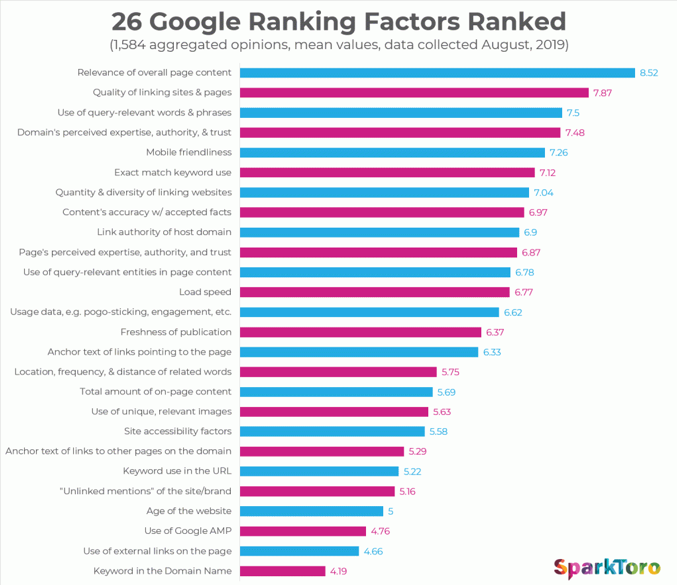
According to Sparktoro, it appears the top Google ranking factors are…
- Relevance of overall page content.
- Quality of linking sites and pages.
- Use of query-relevant words and phrases
- Domain’s perceived Expertise-Authority-Trust A-T)
- Mobile-friendliness.
- Exact match keyword use
- Quantity and diversity of linking websites.
- Content accuracy with accepted facts
- Link authority of host domain
- Page’s perceived Expertise-Authority-Trust
What is E-A-T?
E-A-T has been around awhile, but appears to be coming more influential in Google’s algorithm.
E-A-T is being used more and more in YMYL content. YMYL used to refer to “Your Money, Your Life” subjects; arguably the most important subjects to people. Now, it’s more like Your Money, Your Life, Your Politics, Your Shopping, Your News, Your Religion and Your Education.
Google pays close attention to the Authoritativeness and reputation of the author and the website.
To enhance your street cred in the era of E-A-T, it’s important that you create a good About Me page. Highlight your experience, expertise, credentials, formal education or life experience. Get interviewed on a podcast or in a magazine and link to any and all content that supports you as an authority.
E-A-T Guidelines
The About Page should discuss the authors and the site itself. Make yourself discoverable on other platforms; YouTube, Podcasts, eBooks, speaking engagements, guest posts and print publications.
Display and link to professional credentials or life experience, especially in YMYL niches.
Many bloggers cannot establish E-A-T.
It’s important for search engine rankings, and also for your audience to know, like and trust you.
Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines
Google has hired thousands of people for human review of our websites. We’re not really sure how they operate, but we think their work is focused on YMYL content and E-A-T.
We believe their reviews are part of the equation for ranking our sites, based on Expertise and Authority and if our content is ‘satisfying’ and relevant.
The guideline document is an outline. Not theory or philosophy.
It’s a new wrinkle. Human review.
Google’s Danny Sullivan explains, “Our systems aren’t looking for EAT. Our raters are using that to see if our systems are working well to show good information. There are many different signals that, if we get it right, align with what a good human EAT assessment would be.”
If we understand how Google’s quality raters learn to assess content for Google, it may help us do better in search engine optimization of our content. Knowing what questions to ask of your own content will give you a better chance of ranking better.
Google's Quality Rater Guidelines. What questions are they asking? If you learn how the raters assess content, you'll do better in search. Share on XWe can learn more from Google’s Webmaster Blog.
Content and Quality Questions
 Does the content provide original information, reporting, research or analysis?
Does the content provide original information, reporting, research or analysis?- Does the content provide a substantial, complete or comprehensive description of the topic?
- Does the content provide insightful analysis or interesting information that is beyond obvious?
- If the content draws on other sources, does it avoid simply copying or rewriting those sources and instead provide substantial additional value and originality?
- Does the headline and/or page title provide a descriptive, helpful summary of the content?
- Does the headline and/or page title avoid being exaggerating or shocking in nature?
- Is this the sort of page you’d want to bookmark, share with a friend, or recommend?
- Would you expect to see this content in or referenced by a printed magazine, encyclopedia or book?
Expertise Questions
- Does the content present information in a way that makes you want to trust it, such as clear sourcing, evidence of the expertise involved, background about the author or the site that publishes it, such as through links to an author page or a site’s About page?
- If you researched the site producing the content, would you come away with an impression that it is well-trusted or widely-recognized as an authority on its topic?
- Is this content written by an expert or enthusiast who demonstrably knows the topic well?
- Is the content free from easily-verified factual errors?
- Would you feel comfortable trusting this content for issues relating to your money or your life?
Presentation and Production Questions
 Is the content free from spelling or stylistic issues?
Is the content free from spelling or stylistic issues?- Was the content produced well, or does it appear sloppy or hastily produced?
- Is the content mass-produced by or outsourced to a large number of creators, or spread across a large network of sites, so that individual pages or sites don’t get as much attention or care?
- Does the content have an excessive amount of ads that distract from or interfere with the main content?
- Does content display well for mobile devices when viewed on them?
Comparative Questions
- Does the content provide substantial value when compared to other pages in search results?
- Does the content seem to be serving the genuine interests of visitors to the site or does it seem to exist solely by someone attempting to guess what might rank well in search engines?
Does your content meet these criteria?

Relevance
Simply providing the ‘perfect answer’ to a search query will get your content ranked, especially when creating ‘Response’ posts. (See below.)
Resist the urge to write opinion pieces. Select a keyword, or even better, a search query you have seen your target audience use, and enter it into Google, then the letter ‘a’ and see what Google autocomplete shows you. Then the letter ‘b’ and so on. Google is telling you what related queries it has received.
Keyword Research
 This is called The Alphabet Soup Method to keyword research and it can be amazingly effective.
This is called The Alphabet Soup Method to keyword research and it can be amazingly effective.
Keyword research tools are often off significantly in their estimates of monthly traffic. The Alphabet Soup Method is based on information supplied by Google.
Look at who is ranking for what queries. Can you beat them? How long is the ranking content? How many outbound links do they have? Can you make your content more comprehensive and satisfying? Can you get more inbound links?
You won’t be able to beat authority sites ranking in the Top 10.
Most bloggers with similar Domain Authority and forum content in general is easy to beat.
See my list of Best Keyword Research Tools
Guide to On-Page SEO
Most people will tell you that the longer the content, the higher it will rank. Some studies have shown that content with 2,000+ words is almost a requirement to rank on page 1 of the SERPs.
That’s true.
Sometimes.
Some content ranks #1 at 1,000 words and beats longer content because it is more in-depth.
3 Types of Blog Posts
 These 3 types of content; Responsive Posts, Staple Posts and Pillar Posts will cover the different types of searches and site objectives. Some content can be created quickly. Other content takes longer.
These 3 types of content; Responsive Posts, Staple Posts and Pillar Posts will cover the different types of searches and site objectives. Some content can be created quickly. Other content takes longer.
All 3 types have a role in your strategy.
If you’re a beginner blogger or trying to rehabilitate an existing site, it’s actually best to create content in order, beginning with Responsive Posts, then Staple Posts and Pillar Posts last.
Responsive posts are the best place to start and get quick wins. Responsive Posts answer a specific question in your niche that someone is searching for on Google. Analyze what sites are currently ranking on page 1 for a particular query and figure out how to make your answer more comprehensive or helpful.
These are easiest to rank for, especially if you’re just starting out. Google will notice that you are ranking high for certain long-tail terms, which may help your reputation when you create staple and pillar posts.
Responsive Posts (800-1,250 words) are usually very narrow in focus, answering a common, but specific query, such as “How to Grow Tomatoes in a Pot,” rather than more competitive and broader queries, like “How to Grow Vegetables.”
Responsive Posts should only take an hour or so to create.
Write about 15 Responsive posts before moving on to Staple Posts.
Staple Posts (1,500-3000 words) are shareable content like “21 Ways to Do (Something)” or “15 Unbelievable Tips” type posts. As with all 3 of these types of posts, the headline should contain the Focus Keyword.
Write about 15 Staple Posts before moving on to Pillar Posts.
 Pillar Posts (3,500+ words) Pillar content gets shared a lot and they can dominate search engines because they can rank for dozens of keywords even though you should optimize for one Focus Keyword and 2-3 related or ‘semantic’ keywords. They can take hours or a whole day to write.
Pillar Posts (3,500+ words) Pillar content gets shared a lot and they can dominate search engines because they can rank for dozens of keywords even though you should optimize for one Focus Keyword and 2-3 related or ‘semantic’ keywords. They can take hours or a whole day to write.
If you’re writing long-form content, remember to keep it easier to scan, and not a wall of text by ‘chunking’ the content. Make sure you write easy to read short paragraphs, sub-headlines and bullet points. Also, break up content with pictures.
Guides can rank very well because they are comprehensive. SEO expert Neil Patel’s top 3 blog posts are all guides, including Beginner’s Guide to Google Webmaster Tools and Affiliate Marketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide. His site gets millions of visitors every MONTH and he ranks for more than a million keywords.
Once you’ve written a few Pillar Posts, you’ll have a total of 35-40 pieces of content and you should have a handful of keywords ranking and delivering organic traffic to your site.
But, again, it could take weeks. Don’t give up.
Go back and mix it up with Responsive, Staple and Pillar posts, writing a few of each every month. Be consistent.
You may want to avoid creating content that authority sites dominate the SERPs for. Instead, go for a long-tail version of the query with less competition.
Every article you write should link to 2 or 3 other related articles on your site. This helps with SEO, drives more page views on the site, and gives readers somewhere to go if they want to learn more.
What are Content SILOs
One of the recent trends in SEO is creating content SILOs. Rather than having your blog page link to every post you’ve ever written in multiple categories, silo your content into 4-6-8 categories and only link to posts from the same categories. Rather than having “Blog” on your NAV bar, you will link to each ‘category’ instead.
Here’s an example from ProBlogger.

If you have a financial blog, you might write about credit cards, 401K accounts and mortgages, but you shouldn’t link credit card content to mortgage content or vice-versa. Instead, have your Home page link to each of the category pages as if each category was a separate website.
It helps Google index your site’s content more effectively and it helps keep readers in similar content.
Competitive Analysis for Bloggers
Successful bloggers know who their competitors are; what content they create; how long it is and how high they rank.
It is important that you beat them on every piece of content.
First, create a list of at least 10 direct competitors. If you don’t know at least 10 of them, you can find your competitors by doing a search on all keywords you’ve optimized your site for.
If you tried optimizing for 50 keywords, then your list of the Top 10 URLs for each of 50 keywords would be 500 lines in a spreadsheet.
If that’s too much work for you, you can start by finding competitors for keywords you’re actually ranking for, as opposed to the ones you’ve tried to optimize for. There are a number of places you can determine what keywords you (or a competitor) are ranking for, including Ubersuggest.com.
As you evaluate your competitors, you will find some similarities. What content ideas do they share – what common keywords?
Which competitors rank well for attractive keywords that others don’t?
You should only try and compete with other sites that have a similar Domain Authority, usually within 15 or 20 points of yours. If your DA is 15, you will not be able to compete effectively with a DA-55 site until you bring your DA up closer.
What is Domain Authority?
Domain Authority (DA) is a search engine ranking score developed by SEO software company Moz that predicts how well a website will rank on search engine result pages (SERPs) on a scale of 1 to 100 with 100 being best.
Domain Authority is calculated by evaluating multiple factors, including linking root domains and the number of total links, into a single DA score.
Domain authority between 40 and 50 is considered average, between 50 and 60 is considered good. Domain Authority of 60 or above is considered excellent.
Test your site’s Domain Authority using the free MOZ Domain SEO Analysis Tool or try Ahrefs Website Authority Checker. You may notice the two tools will not exactly match Domain or Page Authority.
Types of Blog Content
In my course, WebsiteSuccessEssentials.com, we talk about as many as 15 different types of content that can be created. For SEO purposes, we will concentrate primarily on written content for our content marketing strategy.
One of the considerations of a content creation strategy is how will it be shared? Who will amplify the content? As you can see from the image below, people love to share infographics and lists.
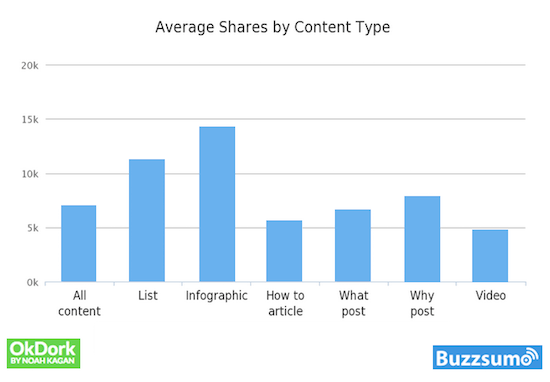
- Lists
- Infographics
- How-to articles
- “What” posts (articles whose title started with the word “What”)
- “Why” posts (articles that tried to answer a “Why” question)
By the way, 10 is the magic number for lists. 10 item lists on average received the most social shares with 10,621 social shares, according to OKDork and BuzzSumo. Top 10 lists had four times as many social shares on average than the second most popular list number (23). The other runner-ups are lists of 16 and 24.
Featured Snippet Optimization
What are Featured Snippets?
Featured snippets are answer boxes below the ads at the top of Search results. They are appealing because of the voice search component.
Featured snippets, AKA “answer boxes,” aim at answering the user’s question right away. Being featured means getting additional brand exposure in search results.
The Featured Snippet box is often referred to as “Position #0” because it appears above the traditional #1 spot.
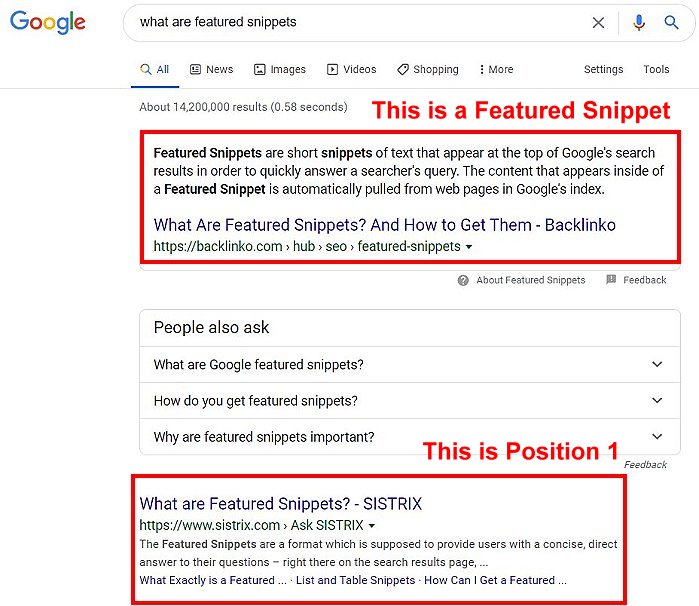
According to Search Engine Land, Featured Snippets get ~ 8% of all clicks.
41% of featured snippets come from questions. And most results come in lists.
ProTip: If Google is showing 8 results of a list, then include more so that people click on the full list.
74% of Google queries will have a snippet.
Rich snippets pull information from a blog post that specifically answers a search query. There is also a link to the blog post that the snippet came from.
The first few sentences are important. Sure, you establish a rapport with the reader, but you are also keying up content. Tell them, “I have the answer to your question.”
76% of snippets come from the first 500 words of an article.
Successful blogs posts should have content intended to be the snippet.
Format Your Content to be Noticed
Paragraph-style answer targets make up half of all snippets.
- Paragraph-style (50%)
- List-style (27%)
- Video (16%)
Format a single paragraph is a way that Google likes; bolded. Often the best 2 or 3-sentence summary jumps authority sites with more backlinks.
Unique Blogging Ideas
Don’t write the obvious. It won’t get people excited. They won’t read it or share it. Original content works very well because people have not seen it anywhere else. Surveys are a great way to generate original content.
Technical Guide to SEO
Three of the most important elements of technical SEO, are having an SSL Certificate on your site, whether you accept money or not; site loading speed, especially on mobile; and being mobile-friendly.
SSL is something you typically get from your web host. It can be free or there can be a cost, depending on a number of things. Ask your hosting company. It’s often free on sites with a cPanel.
Site loading speed is an important ranking factor to Google, especially for sites loading on mobile devices. Google began “mobile-first” indexing in July 2019. You can check your site’s speed with Google PageSpeed Insights.
A score of 50+ is probably OK, but you can follow the recommendations to optimize and fix your site for faster loading. You can get similar information from the Pingdom Website Speed Test.
For Technical SEO, these are your primary Ranking Factors
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
- Site Speed
- Mobile Ready
- Lack of Malware
- Short URLs
- Easy Navigation
- Schema Usage
Google expects at least one image per page and images can help create content that converts. Images can be optimized for SEO by using keywords in filenames and image ALT tags.
Google apparently checks how many broken links are on the site and if there are copyright issues. There may also be penalties for over-monetization and spammy affiliate links.
For more technical SEO, see the section below, “More SEO Best Practices,” which outlines techniques we don’t always see website owners and managers implementing, perhaps because they are technical. But XML Sitemaps and the robot.txt file can be very helpful in getting your pages indexed and are not too difficult to create.
More SEO Best Practices 2020
In addition to the recommendations above concerning Technical SEO (Mobile -responsive, fast page loading speeds and using HTTPS) we often see people fail to edit their meta descriptions. Meta descriptions are a signal to Google about what the page content is about and should contain your Focus Keyword and maybe a related keyword.
But the other benefit of a well-written meta description is that it is what shows up on the SERPs, so you write one to confirm to the viewer that you have the information they’re looking for AND include a benefit of clicking to your site.
Meta descriptions should be 155 characters or less.
Always use an XML Sitemap.
What are XML sitemaps? Sitemaps are machine code that search engine crawlers use to index a website. You can actually have multiple XML sitemaps, including one for webpages. Sites also can have image sitemaps which document information about images on the site and the third most common sitemaps are video sitemaps of pages containing embedded videos.
 XML sitemaps were created after HTML sitemaps. HTML sitemaps, created using HTML (HyperText Markup Language) were created to help power users find information quickjly using a more complex form of site navigation than the site’s main NAV menu. They are not as common as they once were.
XML sitemaps were created after HTML sitemaps. HTML sitemaps, created using HTML (HyperText Markup Language) were created to help power users find information quickjly using a more complex form of site navigation than the site’s main NAV menu. They are not as common as they once were.
If you’re using WordPress, XML sitemaps can be automatically generated using a plugin. Any time you create or update content, the sitemaps are automatically updated.
Sitemaps should be referenced in your sites robot.txt file. You can see them at domain.com/robots.txt.
What is a robots.txt file?
A robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which pages or files the crawler should or shouldn’t index on your site. Robots.txt files were created to avoid overloading site with requests. SEOs began using it to keep certain pages out of the public index, such as download or ‘thanks for subscribing’ pages. Google prefers that we use noindex directives, or password-protect those pages instead.
What is robots.txt used for?
Robots.txt is used primarily to manage crawler traffic to your site, and usually to keep a page off Google, depending on the file type: webpages, audio/video files and other resources.
You should know that not all search engines interpret robots.txt directives in the same manner.
A robotted page can sometimes be indexed, even if the robot file asks the search engine not to. This usually happens when another website links to it.
To check the current index status of a URL, you can use Google’s URL Inspection Tool.
Off-Page SEO Tips
 It’s not enough to create a blog. To get traffic you need other owned media, like a YouTube channel or Pinterest strategy. Repurposing your content on Medium.com or LinkedIn exposes it to fresh audiences, whether the links to your site are Follow or No-Follow.
It’s not enough to create a blog. To get traffic you need other owned media, like a YouTube channel or Pinterest strategy. Repurposing your content on Medium.com or LinkedIn exposes it to fresh audiences, whether the links to your site are Follow or No-Follow.
Creating linkable or sharable content should be part of every blog post. Rand Fishkin, the Co-Founder of SEOmoz says you should always be thinking, “Who is going to amplify this?”
Your best external links may come from people linking to your epic content.
Mike Pearson in his Stupid Simple SEO course recommends 2 ways of getting decent backlinks, so I’m sharing them in this guide to SEO.
#1 HARO: Help A Reporter Out gives journalists and industry experts a free and easy way to connect.
Journalists post requests via the HARO platform for quotes on specific topics and industries, which subscribers receive 3X daily by email. These sources then send responses to requests that interest them. The journalists work in various media, including print, audio and video.
You have to be quick to respond. Some requests get answered within an hour.
#2 Quora: Quora is basically a site where anyone can ask or answer questions. You can build your brand by monitoring questions that are asked in your niche and answer them. Sign up and list the topics you know best.
When you answer questions, you can provide links for more information. Start here.
ProTip: Try and link to blog posts that relate to the question being asked. Give them a paragraph or two and then say something like, “I blogged about this and to learn more, click here.”
What Doesn’t Work in SEO
Guest posting has fallen out of favor. Sites worth guest-posting on are hit up too many times and the site’s owners don’t even bother to respond to guest-posting requests.
OR, they ask you to pay them, which is a Google no-no.
It’s a waste of your valuable time.
Guest blogging used to be an effective tactic for exposing your brand to new audiences and getting an external link, but Google knows the technique is being abused and has devalued or in some cases penalized those who participate.
Update: John Mueller, the Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google, just said (Aug 10, 2020) that links from guest blog posts have zero value. He said on Twitter when asked about that as a link building strategy, he said “those links have zero value.” “It’s a waste of time if you’re just doing it for the links,” John added.
That said, if you get asked to write a guest post or an article in an offline publication, there can be benefits. Just don’t allow it to look spammy.
Writing articles for media properties like Entrepreneur.com and Huffington Post also used to be more effective than it is today. Everybody benefitted from a backlink for big authority sites and, while it may expose you to a new audience, the SEO benefits are not as juicy.
There was also a time when finding a broken link to a competitor on someone’s site and telling the owner that they had a broken link and asking them to link to similar content on your site worked well. It’s really a waste of time now. Much better to create awesome content that gets links.
All of these tactics seem a little spammy, don’t they? The work can be hard and the results meager.
The 80/20 Rule of Blogging
Blog content creators should spend time promoting their content, but how much and how?
Some experts recommend spending 4X as much time promoting or marketing a blog as they do writing it. Experts say it takes an average of nearly 4 hours (3:57) to create a blog post. If you spend 20% (4 hours) of your time creating the content, you should spend 16 hours promoting it in non-spammy ways.
But I know several successful bloggers who argue that if you spend 95% of your time creating content, you will create not only more content, but more comprehensive content. In this case, I think they are counting on getting more shares and links with more content creation efforts.
Guide to SEO Recap
Search Engine Optimization is always evolving. Google makes minor algorithm changes daily and more significant updates monthly. This is all done to benefit the searchers using Google to find information, solutions and products.
One of the most important things we can do as content creators is to create relevant, comprehensive content and a lot of it. We need to cross link it using the SILO approach.
We need to create it and be patient.
External links are important signals to Google, but traditional linkbuilding is no longer effective. We need to create content that people will amplify and share with their tribes.
As you create new content or re-assess existing content, ask the questions the Quality Raters are using to analyze websites and blogs.
Use The Alphabet Soup Method of keyword research. Use one Focus Keyword per article for Responsive Posts and format the first 500 words for the Featured Snippet.
Use on Focus Keyword for all of your content, but use dozens of related keywords to make your Staple Posts and Pillar Posts.
SILO your content. Crosslink to related articles only.
Make sure your site loads quickly, is mobile responsive and has an SSL certificate.
Use short, keyword-rich URLs.
Get some links from people who think your content is awesome!
Link to your content from Medium, Pinterest, YouTube, HARO and Quora.
We’ve covered a lot in this Guide to Search Engine Optimization. What questions do you have? What can you share of your own experiences?




 Does the content provide original information, reporting, research or analysis?
Does the content provide original information, reporting, research or analysis? Is the content free from spelling or stylistic issues?
Is the content free from spelling or stylistic issues?

